QFX5110 Ethernet Switch Datasheet
Download DatasheetProduct Overview
QFX5110 access and aggregation switches deliver low latency, rich Layer 2 and Layer 3 features, VXLAN overlay deployments, and 100GbE uplinks, making it the industry’s most nimble line of switches.
Featuring L3 gateway capabilities for bridging between virtualized and bare-metal servers, the QFX5110 is designed for extremely agile data centers that demand support for overlay/underlay network architectures. The high-density 10GbE, 40GbE, and 100GbE ports also make the QFX5110 ideally suited for use in data center spine and leaf topologies and campus distribution..

Product Description
Data centers are rapidly adopting cloud services, whether completely off-premises models or hybrid models with critical services offered through on-premise private clouds. The tremendous growth of off-premises cloud services, coupled with the widespread adoption of overlay technologies, has created a need for highly agile switching platforms that can satisfy the demands of these evolving data centers.
The high-performance Juniper Networks® QFX5110 line of Ethernet switches fit the bill, providing the foundation for dynamic data centers. As a critical enabler for IT transformation, the data center network supports cloud and SDN adoption, network virtualization, integrated/scale-out storage, and the rapid deployment and delivery of mission-critical applications that significantly increase east-west traffic within the data center. Furthermore, increasing demand for 100GbE spine ports is driving the need for 100GbE uplinks for all server access speeds, including 10GbE and 40GbE. The QFX5110 includes 100GbE uplinks, enabling it to support a diverse set of switching architectures, including fabric, Layer 3, and spine-and-leaf deployments, enabling users to easily adapt as requirements change over time. The QFX5110 switch can be positioned in campus distribution and core deployments.
Architecture and Key Components
The QFX5110 switches include 10GbE (fiber) and 40GbE or 100GbE fixed-configuration options with rich Layer 2, Layer 3, and MPLS features. The QFX5110 switches run the same reliable, high-performance Juniper Networks Junos® operating system that is used by the Juniper Networks QFX5100 family of products, EX Series Ethernet Switches, Juniper Networks routers, and Juniper Networks SRX Series Services Gateways, ensuring a consistent implementation and operation of control plane features across the entire Juniper infrastructure.
QFX5110 Switch Models
The QFX5110 switches are compact, 1 U platforms that provide wire-speed packet performance, very low latency, and a rich set of Junos OS features. In addition to a high-throughput Packet Forwarding Engine (PFE), the performance of the QFX5110 control plane is further enhanced with a powerful 1.8 GHz quad-core Intel CPU with 16 GB of memory and 64 GB SSD storage.
Two QFX5110 switch models are available:
- QFX5110-48S—A 10GbE/100GbE data center access switch, the QFX5110-48S offers 48 small form-factor pluggable plus (SFP+) transceiver ports and four QSFP28 ports that can be configured as 4x40GbE or 4x100GbE ports, with an aggregate throughput of 1.76 Tbps or 1.32 Bpps per switch. For added flexibility, each QSFP28 port can also be configured as 4x10GbE ports using breakout cables, increasing the total number of supported 10GbE ports to 64 per switch.
- QFX5110-32Q—A 40GbE/100GbE data center access and aggregation switch, the QFX5110-32Q offers up to 32 QSFP+ ports, or 20 QSFP+ ports and four QSFP28 ports, with an aggregate throughput of 2.56 Tbps or 1.44 Bpps per switch. For added flexibility, the QSFP+ ports can also be configured as 4x10GbE ports using QSFP+-to-SFP+ direct attach copper (DAC) or QSFP+-to-SFP+ fiber breakout cables and optics, or as 24 4x10GbE and eight QSFP+ ports, increasing the total number of supported 10GbE ports to 96 per switch.
QFX5110 Highlights
The QFX5110 switches feature the following highlights:
- Support high-density, multi-speed configurations for 10/40/100GbE access and aggregation, with up to 64 or 96 10GbE ports, up to four 100GbE uplink ports, and up to 32 40GbE ports in a 1 U platform
- Deliver up to 2.56 Tbps Layer 2 and Layer 3 performance, with latency as low as 550 nanoseconds
- Include a 1.8 GHz quad-core Intel CPU with 16 GB memory and 64 GB SSD storage
- Feature rich automation capabilities with support for Python and zero touch provisioning (ZTP)
- Support virtualization protocols such as Virtual Extensible LAN (VXLAN) and Open vSwitch Database (OVSDB) protocol as L2 Gateway or L3 Gateway
- Offer advanced Junos OS features such as BGP add-path, MPLS, L3 VPN, and IPv6 6PE
Junos OS
The high-performance QFX5110 switches run Junos OS, Juniper’s powerful and robust network operating system that powers all Juniper switches, routers, and firewalls. Key Junos OS features that enhance the functionality and capabilities of the QFX5110 include:
- Software modularity, with process modules running independently in their own protected memory space and with the ability to do process restarts
- Uninterrupted routing and forwarding, with features such as nonstop active routing (NSR) and nonstop bridging (NSB)
- Commit and rollback functionality that ensures error-free network configurations
- A powerful set of scripts for on-box problem detection, reporting, and resolution
Junos OS Software License
The software features supported on the QFX5110 switches are categorized into three tiers: Base, Premium, and Advanced.
- Base software features include basic Layer 2 switching, basic Layer 3 routing, multicast, automation, programmability, zero touch provisioning (ZTP), and basic monitoring. A Base software features license comes with the purchase of the hardware and does not require any explicit license keys.
- Premium software features include all Base license functionality, plus BGP, IS-IS, and EVPN Virtual Extensible LAN (VXLAN) to explicitly address the needs of enterprise customers. To enable these features, customers must purchase the QFX5K-C1-PFL license, generate unique license keys, and install them on the switch. The license is not portable across devices.
- Advanced software features include all Premium license functionality plus MPLS to explicitly address the needs of data center interconnect and edge use cases. To enable these features, customers must purchase the QFX5K-C1-AFL license, generate unique license keys, and install them on the switch. The license is not portable across devices.
The Premium and Advanced software licenses are classified as Class 1, Class 2, Class 3, etc., and offered as perpetual licenses. Class 1 licenses are applicable to the QFX5110-48S and QFX5110-32Q switches. Please see Ordering Information for license SKU descriptions.
Data Center Deployments
Today’s data centers are typically built with high-performance, small form-factor, multicore blade and rack servers. The greater compute capacity and server densities enabled by these devices are increasing traffic volume, creating a need for high-speed, low-latency, storage-converged and I/O-converged networking solutions that can maximize performance for physical servers, virtual servers, and storage.
The QFX5110 switches deliver low-latency, lossless, high-density 10GbE and 40GbE interfaces, as well as 100GbE uplinks to the core network demanded by today’s data center. Furthermore, the QFX5110 offers VXLAN Layer 2 and Layer 3 gateway support, making it an ideal solution for overlay deployments in the data center. All QFX5110 switches are designed to consume the lowest possible power while optimizing space, reducing data center operating costs. Flexible airflow direction options enable the QFX5110 switches to support back-to-front and front-to-back cooling, ensuring consistency with server designs for hot-aisle or cold-aisle deployments.
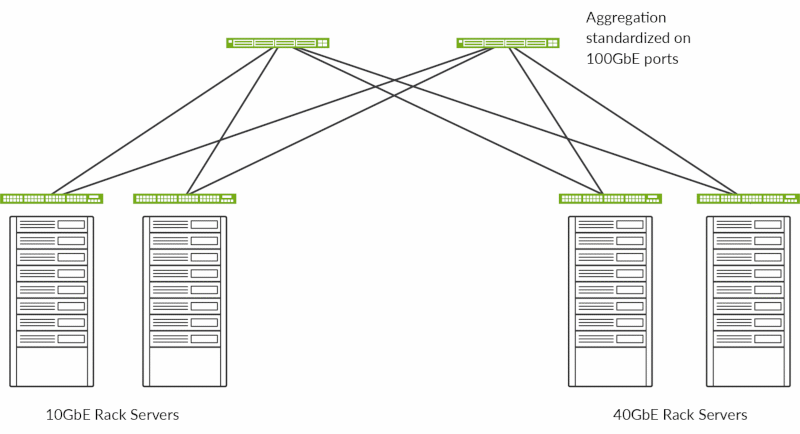
Figure 1: QFX5110 switches supporting a data center server access configuration
Data Center Server Access
The QFX5110 switches are ideal for top-of-rack deployments of various densities and speeds. The QFX5110-48S offers 48 ports of native 10GbE for server connectivity, plus up to four 40GbE or 100GbE ports for uplink connectivity, providing very low oversubscription of 1.2:1 from access to aggregation. Meanwhile, the QFX5110-32Q offers 20 QSFP+ 40GbE ports for server connectivity and up to four 100GbE ports for uplink connectivity, providing an oversubscription of 2:1 from access to aggregation. Each 40GbE port can be further broken out into four 10GbE ports, providing additional options for server connectivity.
The QFX5110 switches can operate in both cut-through and store-and-forward modes, delivering sustained wire-speed switching with sub-microsecond latency and low jitter for any packet size (including jumbo frames) in both modes. All QFX Series switches support extensive Layer 2 features, enabling the device to support high-density 10GbE Layer 2 access deployments. With features such as multichassis link aggregation group (MC-LAG), the QFX5110 supports active/active server dual homing and can utilize full bisectional bandwidth from server to switch. When the QFX5110 is deployed in the access layer, MC-LAG on QFX10000 switches in the aggregation layer provides maximum resiliency and full Layer 2 multipathing in the network.
The Junos OS features the most advanced and robust routing capabilities in the industry. All QFX5110 switches include support for RIP and OSPF for both IPv4 and IPv6 in the base software. Advanced routing capabilities such as IS-IS and BGP are also supported. With additional capabilities like 64-way equal-cost multipath (ECMP) and BGP add path, the QFX5110 is an ideal building block for deploying the most robust Layer 3 underlay for SDN.
Campus Deployments
Juniper Networks campus fabrics provide a single, standards-based Ethernet VPN-Virtual Extensible LAN (EVPN-VXLAN) solution that can be deployed in any campus, whether a two-tier network with a collapsed core distribution or a campus-wide system that involves multiple buildings with separate distribution and core layers.
The QFX5110-48S switch is ideal as campus distribution switches with 10GbE downlinks and 40GbE/100GbE uplinks supporting technologies like MC-LAG and EVPN multihoming.
The QFX5110-32Q switch is ideal as a campus core switch with 32 ports of 40GbE and support for campus fabric with EVPN-VXLAN.
Juniper campus fabrics support these validated architectures:
- MC-LAG and EVPN Multihoming (Collapsed Core/Distribution). A pair of interconnected QFX5110 switches can be deployed to provide EVPN multihoming (ESI-LAG) or multichassis link aggregation (MC-LAG) in a collapsed core/distribution configuration. This eliminates the need for Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) across the campus network by providing multihoming capabilities from the access to the distribution layer, while distribution to the core is an L3 IP fabric. ESI-LAG also supports horizontal scaling with more than two devices in the distribution layer and can extend EVPN to the core.
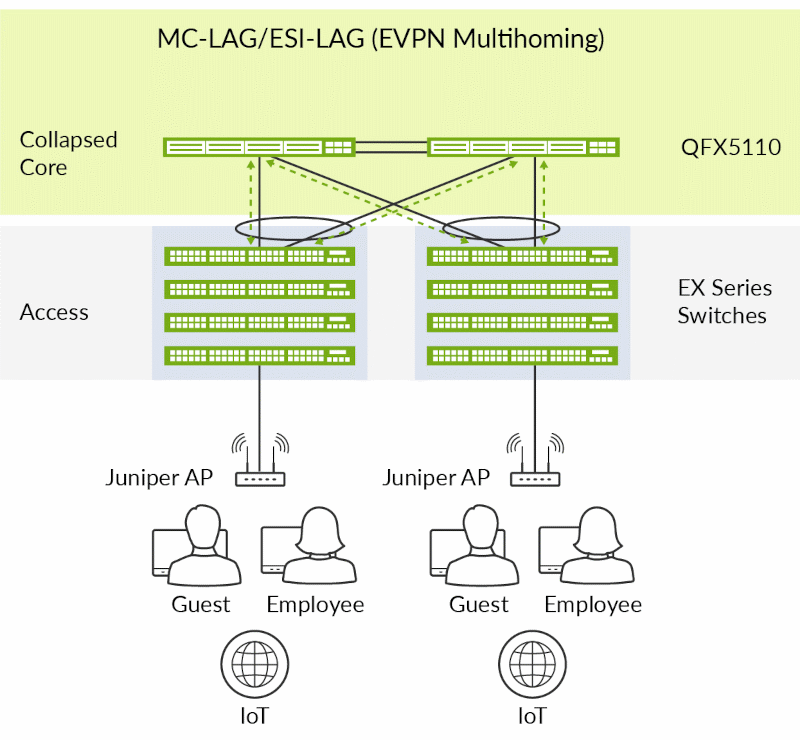
Figure 2: QFX5110 switch as a campus collapsed core/distribution switch with EVPN multihoming (ESI-LAG) and MC-LAG support
- Campus Fabric Core-Distribution. A pair of interconnected QFX5110 switches can provide EVPN L2 and L3 VXLAN gateway support. This eliminates the need for STP across the campus network by providing a multihoming capability from the access to the distribution layer, while distribution to the core is an L3 IP fabric using EVPN technology. The IP fabric can also extend to connect multiple enterprise buildings, while VXLAN allows stretching L2 across buildings. An IP Clos network between the distribution and the core layers can exist in two modes, both of which are supported by the QFX5110 switch:
- Centrally routed bridging overlay: An IRB interface placed at a central location in the fabric (in this case, a core device)
- Edge routed bridging overlay: An IRB interface placed at the edge of the fabric (in this case, a distribution device)
- Campus Fabric IP Clos: The campus fabric IP Clos architecture pushes VXLAN Layer 2/3 gateway functionality to the access layer. In this architecture, the QFX5110 switch acts as an IP fabric distribution switch.
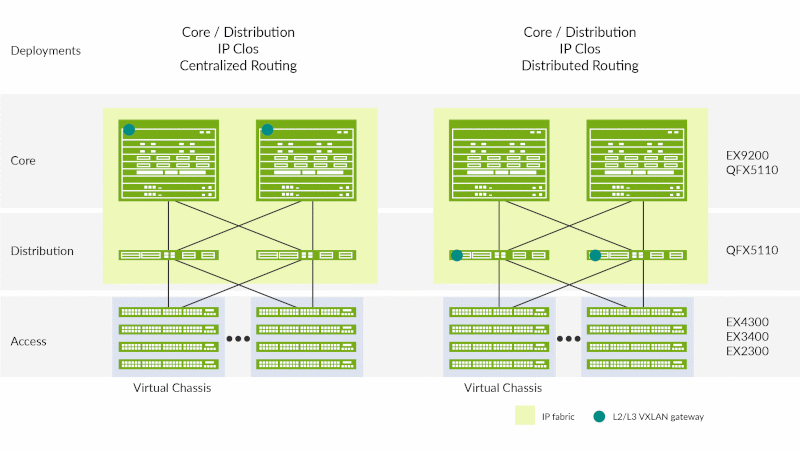
Figure 3: QFX5110 switch as a campus distribution switch with EVPN-VXLAN L2/L3 gateway support
Features and Benefits
- Automation—The QFX5110 switches support a number of features for network automation and plug-and-play operations. Features include zero touch provisioning, operations and event scripts, automatic rollback, and Python scripting. The switch also supports integration with VMware NSX Layer 2 Gateway Services, and OpenStack.
- Flexible Forwarding Table—The QFX5110 includes a Unified Forwarding Table (UFT), which allows the hardware table to be carved into configurable partitions of Layer 2 media access control (MAC), Layer 3 host, and longest prefix match (LPM) tables. In a pure L2 environment, the QFX5110 supports 288,000 MAC addresses. In Layer 3 mode, the table can support 208,000 host entries. In LPM mode, it can support 128,000 prefixes. Junos OS provides configurable options through a CLI so that each QFX5110 can be optimized for different deployment scenarios.
- Intelligent Buffer Management—The QFX5110 switches have a total of 16 MB shared buffers. While 25% of the total buffer space is dedicated, the rest is shared among all ports and is user configurable. The intelligent buffer mechanism in the QFX5110 effectively absorbs traffic bursts while providing deterministic performance, significantly increasing performance over static allocation.
- MPLS—QFX5110 switches support a broad set of MPLS features, including L3 VPN, IPv6 provider edge router (6PE), RSVP traffic engineering, and LDP to allow standards-based network segmentation and virtualization. This enables the QFX5110 to be deployed as a low-latency MPLS label-switching router (LSR).
- VXLAN Overlays—The QFX5110 switch is capable of supporting Layer 2 and Layer 3 gateway services. Customers can deploy overlay networks to provide Layer 2 adjacencies for applications over Layer 3 fabrics. The overlay networks utilize VXLAN in the data plane and EVPN or OVSDB to program the overlays. The overlays can operate without a controller, or they can be orchestrated with an SDN controller.
Management, Monitoring, and Analytics
Data Center Fabric Management: Juniper Apstra provides operators with the power of intent-based network design to help ensure changes required to enable data center services can be delivered rapidly, accurately, and consistently. Operators can further benefit from the built-in assurance and analytics capabilities to resolve Day 2 operations issues quickly.
Apstra Key Features
- Automated deployment and zero-touch deployment
- Continuous fabric validation
- Fabric lifecycle management
- Troubleshooting using advanced telemetry
For more information on Apstra, see Juniper Apstra.
For managing AI-driven campus fabrics, Juniper Mist Wired Assurance brings cloud management and Mist AI to campus fabrics. It sets a new standard moving away from traditional network management towards AI-driven operations, while delivering better experiences to connected devices.
Wired Assurance key features are:
- Automated deployment and zero touch deployment
- Anomaly detection
- Root cause analysis
For more information see Juniper Mist Wired Assurance.
Juniper® Paragon Insights (formerly HealthBot). combines the power of telemetry, programmability, advanced algorithms, and Machine Learning. It delivers the following features and benefits for enhanced monitoring and analytics:
- Key performance indicator collection and visualization
- Anomaly detection
- Root cause analysis
- Automated remediation
- Multivendor support
- Customizable playbooks
- JTI telemetry
For more information see Paragon Insights.
Junos Telemetry Interface
The QFX5110 supports Junos Telemetry Interface (JTI), a modern telemetry streaming tool designed for performance monitoring in complex, dynamic data centers. Streaming data to a performance management system enables network administrators to measure trends in link and node utilization, as well as troubleshoot issues such as network congestion, in real time. JTI provides the following capabilities:
- Application visibility and performance management by provisioning sensors to collect and stream data and analyze application and workload flow path through the network.
- Capacity planning and optimization by proactively detecting hotspots and monitoring latency and microbursts.
- Troubleshooting and root cause analysis via high-frequency monitoring and correlating overlay and underlay networks.
QFX5110 Deployment Options
Table 1 shows some of the many QFX5110 deployment options.
| Port Combinations | Switch | Deployment |
| 48x10GbE + 4x40GbE | QFX5110-48S | Leaf |
| 20x40GbE + 4x100GbE | QFX5110-32Q | Spine |
Figure 4 shows QFX5110 top-of-rack switches deployed with QFX5110-32Q spine switches acting as centralized gateways. In this topology, VXLAN tunnel encapsulation and de-capsulation occur on the QFX5110-32Q spine switches. Other members of the QFX5100 and QFX5200 lines of switches can also be deployed as leaf nodes in this deployment.
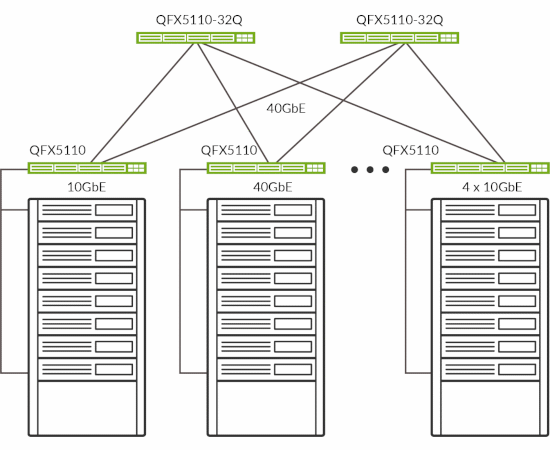
Figure 4: QFX5110-48S and QFX5110-32Q leaf-spine deployment.
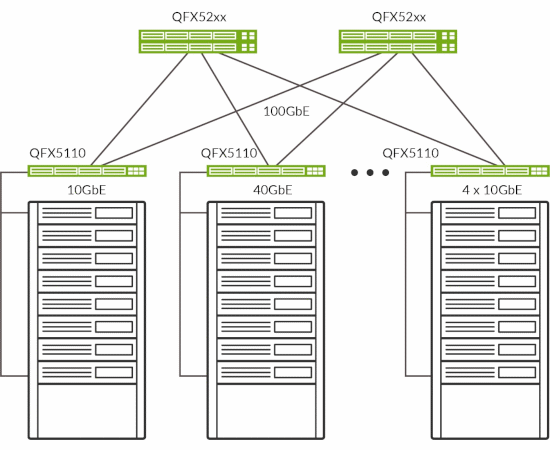
Figure 5: Distributed gateway at leaf with QFX5200/QFX5210 as spine.
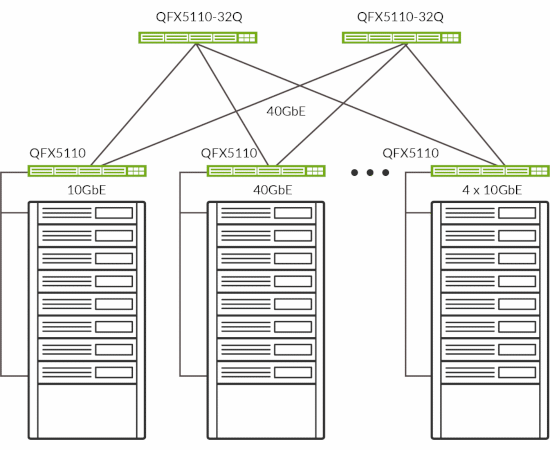
Figure 6: Distributed gateway at leaf with QFX5110-32Q as spine.

| Specification | QFX5110-48S | QFX5110-32Q |
| System Throughput | Up to 1.76 Tbps (bidirectional) | Up to 2.56 Tbps (bidirectional) |
| Forwarding Capacity | 1.32 Bpps | 1.44 Bpps |
| Interface Options |
|
|
| Other Interface Notes |
|
|
| Specification | QFX5110-48S | QFX5110-32Q |
| Dimensions (W x H x D) |
1.72 x17.36 x 20.48 in (4.37 x 44.09 x 52.02 cm) |
|
| Rack units | 1 U | |
| Weight | 23 lb (10.43 kg) | 24.6 lb (11.16 kg) |
| Operating system | Junos OS | |
| CPU | 1.8 GHz quad-core Intel CPU | |
| Power |
|
|
| Cooling |
|
|
| Total packet buffer | 16 MB | |
| Warranty | Juniper standard one-year warranty | |
Power Consumption
| Parameters | QFX5110-32Q | QFX5110-48S |
| Maximum power draw* | 200 W AC | 226 W AC |
| Typical power draw** | 148 W AC | 190 W AC |
| Parameter | Value |
| MAC addresses per system | 288,000 |
| VLAN IDs | 4,093 |
| Number of link aggregation groups (LAGs) | 104 |
| Number of ports per LAG | 32 |
| Firewall filters (ingress / egress) | 6,142 / 1,022 |
| IPv4 unicast routes | 128,000 prefixes; 208,000 host routes; 64 ECMP paths |
| IPv4 multicast routes | 104,000 |
| IPv6 unicast routes | 84,000 |
| IPv6 multicast routes | 52,000 |
| ARP entries | 48,000 |
| Jumbo frame | 9,216 bytes |
| Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) |
|
| Traffic mirroring |
|
Software Features Supported
Layer 2 Features
- STP—IEEE 802.1D (802.1D-2004)
- Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) (IEEE 802.1w); MSTP (IEEE 802.1s)
- Bridge protocol data unit (BPDU) protect
- Loop protect
- Root protect
- RSTP and VSTP running concurrently
- VLAN—IEEE 802.1Q VLAN trunking
- The Routed VLAN Interface (RVI)
- Port-based VLAN
- Private VLAN (PVLAN)
- VLAN translation
- Static MAC address assignment for interface
- Per VLAN MAC learning (limit)
- MAC learning disable
- Link Aggregation and Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) (IEEE 802.3ad)
Link Aggregation
- Multichassis link aggregation (MC-LAG)
- Redundant Trunk Group (RTG)
- LAG load sharing algorithm—bridged or routed (unicast or multicast) traffic:
- IP: SIP, Dynamic Internet Protocol (DIP), TCP/UDP source port, TCP/UDP destination port
- Layer 2 and non-IP: MAC SA, MAC DA, Ethertype, VLAN ID, source port
Layer 3 Features (IPv4)
- Static routing
- Routing protocols (RIP, OSPF, IS-IS, BGP)
- Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP)
- Virtual router
- Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) relay
- Proxy Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
Multicast Features
- Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP): v1, v2, v3
- IGMP snooping: v1, v2, and v3 (Layer 2 only)
- IGMP Filter
- PIM-SM
- Multicast Source Discovery Protocol (MSDP)
Security and Filters
- Secure interface login and password
- RADIUS
- TACACS+
- Ingress and egress filters: Allow and deny, port filters, VLAN filters, and routed filters, including management port filters
- Filter actions: Logging, system logging, reject, mirror to an interface, counters, assign forwarding class, permit, drop, police, mark
- SSH v1, v2
- Static ARP support
- Storm control, port error disable, and autorecovery
- IP source guard
- Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI)
- Sticky MAC address
- DHCP snooping
Quality of Service (QoS)
- L2 and L3 QoS: Classification, rewrite, queuing
- Rate limiting:
- Ingress policing: Single-rate two-color policer, two-rate three-color policer
- Egress policing: Policer, policer mark down action
- Egress shaping: Per queue on each port
- 12 hardware queues per port (8 unicast and 4 multicast)
- Strict-priority queuing (PQ), shaped-deficit weighted round-robin (SDWRR), weighted random early detection (WRED), weighted tail drop
- 802.1p remarking
- Layer 2 classification criteria: Interface, MAC address, Ethertype, 802.1p, VLAN
- Congestion avoidance capabilities: WRED
- Trust IEEE 802.1p (ingress)
- Remarking of bridged packets
Data Center Bridging (DCB)
- Priority-based flow control (PFC)—IEEE 802.1Qbb
- Enhanced transmission selection (ETS)—IEEE 802.1Qaz
- Data Center Bridging Capability Exchange (DCBX), DCBx FCoE, and iSCSI type, length, and value (TLVs)
High Availability
- Sub-second Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD)
- Uplink failure detection
MPLS
- Static label-switched paths (LSPs)
- RSVP-based signaling of LSPs
- LDP-based signaling of LSPs
- LDP tunneling (LDP over RSVP)
- MPLS class of service (CoS)
- MPLS LSR support
- IPv6 tunneling (6PE) (via IPv4 MPLS backbone)
- IPv4 L3 VPN (RFC 2547, RFC 4364)
Server Virtualization Management and SDN-Related Protocols
- VXLAN OVSDB
- EVPN VXLAN
- OpenFlow 1.3 client
Management and Analytics Platforms
- Juniper Apstra for Data Center
- Juniper Mist Wired Assurance for Campus
- Junos Space® Network Director for Campus
- Paragon Insights
Device Management and Operations
- Role-based CLI management and access
- CLI via console, telnet, or SSH
- Extended ping and traceroute
- Junos OS configuration rescue and rollback
- Image rollback
- SNMP v1/v2/v3
- Junos XML management protocol
- sFlow v5
- Beacon LED for port and system
- Zero touch provisioning (ZTP)
- OpenStack Neutron Plug-in
- Python
- Junos OS event, commit, and OP scripts
- Junos Telemetry Interface
Traffic Mirroring
- Port-based
- LAG port
- VLAN-based
- Filter-based
- Mirror to local
- Mirror to remote destinations (L2 over VLAN)
Standards Compliance
IEEE Standard
- IEEE standard
- IEEE 802.1D
- IEEE 802.1w
- IEEE 802.1
- IEEE 802.1Q
- IEEE 802.1p
- IEEE 802.1ad
- IEEE 802.3ad
- IEEE 802.1AB
- IEEE 802.3x
- IEEE 802.1Qbb
- IEEE 802.1Qaz
T11 Standards
- INCITS T11 FC-BB-5
Supported RFCs
- RFC 768 UDP
- RFC 783 Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP)
- RFC 791 IP
- RFC 792 ICMP
- RFC 793 TCP
- RFC 826 ARP
- RFC 854 Telnet client and server
- RFC 894 IP over Ethernet
- RFC 903 RARP
- RFC 906 TFTP Bootstrap
- RFC 951 1542 BootP
- RFC 1058 Routing Information Protocol
- RFC 1112 IGMP v1
- RFC 1122 Host requirements
- RFC 1142 OSI IS-IS Intra-domain Routing Protocol
- RFC 1256 IPv4 ICMP Router Discovery Protocol (IRDP)
- RFC 1492 TACACS+
- RFC 1519 Classless Interdomain Routing (CIDR)
- RFC 1587 OSPF not-so-stubby area (NSSA) Option
- RFC 1591 Domain Name System (DNS)
- RFC 1745 BGP4/IDRP for IP—OSPF Interaction
- RFC 1772 Application of the Border Gateway Protocol in the Internet
- RFC 1812 Requirements for IP Version 4 Routers
- RFC 1997 BGP Communities Attribute
- RFC 2030 SNTP, Simple Network Time Protocol
- RFC 2068 HTTP server
- RFC 2131 BOOTP/DHCP relay agent and Dynamic Host
- RFC 2138 RADIUS Authentication
- RFC 2139 RADIUS Accounting
- RFC 2154 OSPF with Digital Signatures (Password, MD-5
- RFC 2236 IGMP v2
- RFC 2267 Network ingress filtering
- RFC 2328 OSPF v2 (edge mode)
- RFC 2338 VRRP
- RFC 2362 PIM-SM (edge mode)
- RFC 2370 OSPF Opaque LSA Option
- RFC 2385 Protection of BGP Sessions via the TCP MD5 Signature Option
- RFC 2439 BGP Route Flap Damping
- RFC 2453 RIP v2
- RFC 2474 Definition of the Differentiated Services Field (DS Field) in the IPv4 and IPv6 Headers
- RFC 2597 Assured Forwarding PHB (per-hop behavior) Group
- RFC 2598 An Expedited Forwarding PHB
- RFC 2697 A Single Rate Three Color Marker
- RFC 2698 A Two Rate Three Color Marker
- RFC 2796 BGP Route Reflection—An Alternative to Full Mesh IBGP
- RFC 2918 Route Refresh Capability for BGP-4
- RFC 3065 Autonomous System Confederations for BGP
- RFC 3376 IGMP v3 (source-specific multicast include mode only)
- RFC 3392 Capabilities Advertisement with BGP-4
- RFC 3446 Anycast RP
- RFC 3569 SSM
- RFC 3618 MSDP
- RFC 3623 Graceful OSPF Restart
- RFC 4271 Border Gateway Protocol 4 (BGP-4)
- RFC 4360 BGP Extended Communities Attribute
- RFC 4456 BGP Route Reflection: An Alternative to Full Mesh Internal BGP (IBGP)
- RFC 4486 Subcodes for BGP Cease Notification Message
- RFC 4724 Graceful Restart Mechanism for BGP
- RFC 4812 OSPF Restart Signaling
- RFC 4893 BGP Support for Four-octet AS Number Space
- RFC 5176 Dynamic Authorization Extensions to RADIUS
- RFC 5396 Textual Representation of Autonomous System (AS) Numbers
- RFC 5668 4-Octet AS Specific BGP Extended Community
- RFC 5880 Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server
Supported MIBs
- RFC 1155 SMI
- RFC 1157 SNMPv1
- RFC 1212, RFC 1213, RFC 1215 MIB-II, Ethernet-Like MIB and TRAPs
- RFC 1850 OSPFv2 MIB
- RFC 1901 Introduction to Community-based SNMPv2
- RFC 2011 SNMPv2 for Internet Protocol using SMIv2
- RFC 2012 SNMPv2 for the Transmission Control Protocol using SMIv2
- RFC 2013 SNMPv2 for the User Datagram Protocol using SMIv2
- RFC 2233 The Interfaces Group MIB using SMIv2
- RFC 2287 System Application Packages MIB
- RFC 2570 Introduction to Version 3 of the Internet-standard Network Management Framework
- RFC 2571 An Architecture for describing SNMP Management Frameworks (read-only access)
- RFC 2572 Message Processing and Dispatching for the SNMP (read-only access)
- RFC 2576 Coexistence between SNMP Version 1, Version 2, and Version 3
- RFC 2578 SNMP Structure of Management Information MIB
- RFC 2579 SNMP Textual Conventions for SMIv2
- RFC 2580 Conformance Statements for SMIv2
- RFC 2665 Ethernet-like Interface MIB
- RFC 2787 VRRP MIB
- RFC 2790 Host Resources MIB
- RFC 2819 RMON MIB
- RFC 2863 Interface Group MIB
- RFC 2932 IPv4 Multicast MIB
- RFC 3410 Introduction and Applicability Statements for Internet Standard Management Framework
- RFC 3411 An Architecture for Describing SNMP Management Frameworks
- RFC 3412 Message Processing and Dispatching for the SNMP
- RFC 3413 Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Applications—(all MIBs are supported except the Proxy MIB)
- RFC 3414 User-based Security Model (USM) for version 3 of SNMPv3
- RFC 3415 View-based Access Control Model (VACM) for the SNMP
- RFC 3416 Version 2 of the Protocol Operations for the SNMP
- RFC 3417 Transport Mappings for the SNMP
- RFC 3418 Management Information Base (MIB) for the SNMP
- RFC 3584 Coexistence between Version 1, Version 2, and Version 3 of the Internet-standard Network Management Framework
- RFC 3826 The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) Cipher Algorithm in the SNMP User-based Security Model
- RFC 4188 Definitions of Managed Objects for Bridges
- RFC 4318 Definitions of Managed Objects for Bridges with Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol
- RFC 4363b Q-Bridge VLAN MIB
Approvals
Safety
- CAN/CSA-C22.2 No. 60950-1 Information Technology Equipment—Safety
- UL 60950-1 (Second Edition) Information Technology Equipment—Safety
- IEC 60950-1 Information Technology Equipment—Safety (All country deviations): CB Scheme report
- EN 60825-1 Safety of Laser Products—Part 1: Equipment Classification
NEBS
- GR-63-Core Network Equipment, Building Systems (NEBS) Physical Protection
- GR-1089-Core EMC and Electrical Safety for Network Telecommunications Equipment
EMC
- FCC 47CFR, Part 15 Class A USA Radiated Emissions
- ICES-003 Class A
- EN 55022 Class A European Radiated Emissions
- CISPR 22 Class A
- EN 55032 Class A
- CISPR 32 Class A
- EN 55024
- CISPR 24
- EN 300 386
- VCCI Class A Japanese Radiated Emissions
- BSMI CNS 13438 Taiwan Radiated Emissions
- AS/NZS CISPR22
- AS/NZS CISPR32
Environmental Compliance
 Restriction of Hazardous Substances (ROHS) 6/6
Restriction of Hazardous Substances (ROHS) 6/6
 Silver PSU Efficiency
Silver PSU Efficiency
 Recycled material
Recycled material
 Waste Electronics and Electrical Equipment (WEEE)
Waste Electronics and Electrical Equipment (WEEE)
 Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH)
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH)
 China Restriction of Hazardous Substances (ROHS)
China Restriction of Hazardous Substances (ROHS)
Telco
- Common Language Equipment Identifier (CLEI) code
Environmental Ranges
| Parameters | Value |
| Operating temperature | 32° to 104° F (0° to 40° C) |
| Storage temperature | -40° to 158° F (-40° to 70° C) |
| Operating altitude | Up to 2,000 ft (610 m) |
| Relative humidity operating | Operating: 5% to 90% (noncondensing) |
| Relative humidity non-operating | Non-operating: 0% to 95% (noncondensing) |
Juniper Networks Services and Support
Juniper Networks leads the market in performance-enabling services designed to accelerate, extend, and optimize your deployments. Our services enable you to maximize operational efficiency, reduce costs, and minimize risk while achieving a faster time-to-value for your network.
By leveraging best practices from across the industry, you get the maximum levels of system performance, designed and delivered by the world’s leading professional technology experts.
For more information, please visit https://www.juniper.net/us/en/products.html.
Ordering Information
| Product Number | Description |
| Switch Hardware | |
| QFX5110-48S-AFI | QFX5110, 48 SFP+ and 4 QSFP28, back-to-front AC |
| QFX5110-48S-AFO | QFX5110, 48 SFP+ and 4 QSFP28, front-to-back AC |
| QFX5110-48S-DC-AFI | QFX5110, 48 SFP+ and 4 QSFP28, back-to-front DC |
| QFX5110-48S-DC-AFO | QFX5110, 48 SFP+ and 4 QSFP28, front-to-back DC |
| QFX5110-32Q-AFI | 32 QSFP+/20 QSFP+ QSFP28, back-to-front AC |
| QFX5110-32Q-AFO | 32 QSFP+/20 QSFP+ QSFP28, front-to-back AC |
| QFX5110-32Q-DC-AFI | 32 QSFP+/20 QSFP+ QSFP28, back-to-front DC |
| QFX5110-32Q-DC-AFO | 32 QSFP+/20 QSFP+ QSFP28, front—to-back DC |
| QFX5110-FANAFI | QFX5110-FANAFI fan model, back-to-front airflow |
| QFX5110-FANAFO | QFX5110-FANAFO fan model, front-to-back airflow |
| JPSU-650W-AC-AFO | Juniper 650W AC power supply (port-side-to-FRU-side airflow) |
| JPSU-650W-AC-AFI | Juniper 650W AC power supply (FRU-side-to-port-side airflow) |
| JPSU-650W-DC-AFO | Juniper 650W DC power supply (port-side-to-FRU-side airflow) |
| JPSU-650W-DC-AFI | Juniper 650W DC power supply (FRU-side-to-port-side airflow) |
| Optics and Transceivers | |
| QFX-SFP-1GE-T | SFP 1000BASE-T copper transceiver module for up to 100 m transmission on Category 5 |
| QFX-SFP-1GE-SX | SFP 1000BASE-SX GbE optics, 850 nm for up to 550 m transmission on multimode fiber |
| QFX-SFP-1GE-LX | SFP 1000BASE-LX GbE optics, 1,310 nm for 10 km transmission on single-mode fiber |
| QFX-SFP-10GE-USR | SFP+ 10GbE ultra short reach optics, 850 nm for 10 m on OM1, 20 m on OM2, 100 m on OM3 multimode fiber |
| QFX-SFP-10GE-SR | SFP+ 10GBASE-SR 10GbE optics, 850 nm for up to 300 m transmission on multimode fiber |
| QFX-SFP-10GE-LR | SFP+ 10GBASE-LR 10GbE optics, 1310 nm for 10 km transmission on single-mode fiber |
| QFX-SFP-10GE-ER | SFP+ 10GBASE-ER 10GbE optics, 1,550 nm for 40 km transmission on single-mode fiber |
| EX-SFP-10GE-ZR | SFP+ 10GBASE-ZR 10GbE optics, 1,550 nm for 80 km transmission on single-mode fiber |
| QFX-SFP-DAC-1M | SFP+ 10GbE Direct Attach Copper (twinax copper cable), 1 m |
| QFX-SFP-DAC-3M | SFP+ 10GbE Direct Attach Copper (twinax copper cable), 3 m |
| QFX-SFP-DAC-5M | SFP+ 10GbE Direct Attach Copper (twinax copper cable), 5 m |
| QFX-SFP-DAC-1MA | SFP+ 10GbE Direct Attach Copper (active twinax copper cable), 1 m |
| QFX-SFP-DAC-3MA | SFP+ 10GbE Direct Attach Copper (active twinax copper cable), 3 m |
| QFX-SFP-DAC-5MA | SFP+ 10GbE Direct Attach Copper (active twinax copper cable), 5 m |
| QFX-SFP-DAC-7MA | SFP+ 10GbE Direct Attach Copper (active twinax copper cable), 7 m |
| QFX-SFP-DAC-10MA | SFP+ 10GbE Direct Attach Copper (active twinax copper cable), 10 m |
| JNP-QSFP-40G-LX4 | 40GbE QSFP+ LX4 optics |
| QFX-QSFP-40G-SR4 | QSFP+ 40GBASE-SR4 40GbE optics, 850 nm for up to 150 m transmission on multimode fiber |
| QFX-QSFP-40G-ESR4 | QSFP+ 40GBASE-SR4 40GbE optics, 850 nm for up to 300 m transmission on multimode fiber |
| JNP-QSFP-40GE-IR4 | QSFP+ 40GBASE-LR4 40GbE optics for up to 1 km transmission over single-mode fiber |
| JNP-QSFP-4x10GE-IR | QSFP+ 40GBASE-LR4 40GbE optics for up to 1 km transmission over parallel single-mode fiber |
| JNP-QSFP-40G-LR4 | 40GbE QSFP+ LR4 |
| EX-QSFP-40GE-DAC-50CM | 40GbE QSFP+ 0.5 m Direct attach |
| QFX-QSFP-DAC-1M | QSFP+ to QSFP+ Ethernet Direct Attach Copper (twinax copper cable), 1 m passive |
| QFX-QSFP-DAC-3M | QSFP+ to QSFP+ Ethernet Direct Attach Copper (twinax copper cable), 3 m passive |
| JNP-QSFP-DAC-5M | QSFP+ to QSFP+ Ethernet Direct Attach Copper (twinax copper cable), 5 m passive |
| JNP-QSFP-DAC-7MA | 40GbE QSFP+ 7 m, direct attach |
| JNP-QSFP-DAC-10MA | 40GbE QSFP+ 10 m, direct attach |
| QFX-QSFP-DACBO-1M | QSFP+ to SFP+ 10GbE Direct Attach Breakout Copper (twinax copper cable), 1 m |
| JNP-QSFP-DACBO-5MA | QSFP+ to SFP+ 10GbE Direct Attach Breakout Copper (twinax copper cable), 5 m active |
| JNP-QSFP-DACBO-7MA | QSFP+ to SFP+ 10GbE Direct Attach Breakout Copper (twinax copper cable), 7 m active |
| JNP-QSFP-DACBO-10M | QSFP+ to SFP+ 10GbE Direct Attach Breakout Copper (twinax copper cable), 10 m active |
| JNP-QSFP-100G-SR4 | QSFP28 100GbE, SR4, 100 m |
| JNP-QSFP-100G-CWDM | QSFP28 100GbE, CWDM4, 2 km |
| JNP-QSFP-100G-LR4 | QSFP28 100GbE, LR4, 10 km |
| JNP-100G-AOC-1M | QSFP28, 100GbE, AOC, 1 m |
| JNP-100G-AOC-3M | QSFP28, 100GbE, AOC, 3 m |
| JNP-100G-AOC-5M | QSFP28, 100GbE, AOC, 5 m |
| JNP-100G-AOC-7M | QSFP28, 100GbE, AOC, 7 m |
| JNP-100G-AOC-10M | QSFP28, 100GbE, AOC, 10 m |
| JNP-100G-AOC-15M | QSFP28, 100GbE, AOC, 15 m |
| JNP-100G-AOC-20M | QSFP28, 100GbE, AOC, 20 m |
| JNP-100G-AOC-30M | QSFP28, 100GbE, AOC, 30 m |
| Software Feature Licenses | |
| QFX5K-C1-PFL | QFX5000 Class 1 Premium Feature License |
| QFX5K-C1-AFL | QFX5000 Class 1 Advanced Feature License |
About Juniper Networks
At Juniper Networks, we are dedicated to dramatically simplifying network operations and driving superior experiences for end users. Our solutions deliver industry-leading insight, automation, security and AI to drive real business results. We believe that powering connections will bring us closer together while empowering us all to solve the world’s greatest challenges of well-being, sustainability and equality.
1000605 - 015 - EN NOVEMBER 2023

